Know about AlwaysOn Availability Groups in SQL Server

The AlwaysOn Availability Groups in SQL Server were first introduced in SQL Server 2012 replacing the prior Database Mirroring techniques for configuring High Availability on SQL Server databases. This feature was designed in SQL Server to meet the ever-increasing need for ‘High Availability’. Let’s understand what is Always On Availability Groups in detail.
The AlwaysOn Availability Groups is a high availability and disaster recovery solution that acts as an alternative to database mirroring. It allow user to configure groups of databases that can fail over together if there is issue in the host server.
Table of Content
An Introduction to AlwaysOn Availability Groups in SQL Server
The Availability Groups can be used for multiple databases improving cross-database referencing during Failover while Traditional mirroring & clustering method works only for a single database. Another benefit is that user can create multiple failover targets, which is not possible in Database mirroring as it allows only one failover partner. Multiple replicas of an availability group in SQL Server can be generated allowing administrator to make one of them as read only, which can be used for reporting purpose.
More About AlwaysOn Availability Groups
An Availability Group in SQL Server supports a failover environment for a set of user databases, known as Availability Databases that fail over together. It supports set of primary databases and one to eight sets of corresponding secondary databases. Each Availability Database set is hosted by an Availability Replica.
There are two types of Availability Replicas- Single Primary Replica that host the primary databases and One to Eight Secondary Replicas, each of which hosts a set of secondary databases. It acts as potential failover targets for the availability group in SQL Server. An Availability group fails over at the level of an availability replica.
Primary Replica makes primary database available for read-write connections from clients. The process of Data Synchronization occurs at database level where primary replica sends records of transaction log of each primary database to every secondary database.
Transaction log records are cached by every secondary replica and are applied to its corresponding secondary database. Hence, failure of one secondary database will not affect other secondary databases and similarly for primary database.
How to Deploy AlwaysOn Availability Groups in SQL Server
A Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC) is required to deploy AlwaysOn Availability Groups. Every Availability Replica of given availability group must reside on a different mode of same WSFC cluster. The cluster will monitor WSFC Resource group created for each availability group in SQL Server made to check the primary replica’s health.
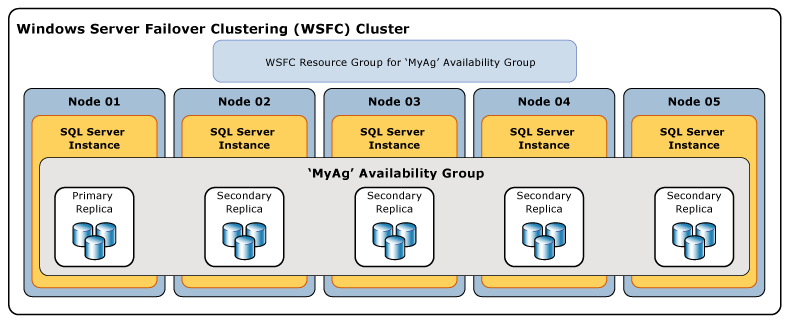
The Above example shows an availability group in SQL Server having one primary replica and four secondary replicas. The WSFC Resource Group is created for ‘MyAg’ Availability Group. All replicas stay at different nodes of the cluster.
Also Read: How to Fix SQL Server Error 7929
Terminologies Used in AlwaysOn Availability Groups
-
Availability Databases
The database that needs to be added to the Availability Group in SQL Server should be online, read-write database that exists on server instance and host the primary replica. Once the database is added, it is joined as a primary database in the availability group. No secondary database is created until backup of new primary database is restored to server instance that host secondary replica.
-
Availability Replicas
An Availability Group in SQL Server defines sets of two/more failover partners known as availability replicas. A copy of availability database is hosted by every Availability replica. Replicas must be hosted by different instances on SQL Server residing on various nodes of WSFC cluster for a single Availability group. Role of primary replica is to host read-write primary database & secondary replica for read only Secondary database.
-
Availability Modes
The task of Availability mode in Alwayson availability groups in SQL server is to check if the primary replica waits to commit transactions on a database until secondary replica has written the records of transaction logs to disk. It has two modes:
Asynchronous-Commit Mode
Asynchronous-commit replica is the availability replica in SQL Server that uses asynchronous-commit mode. In this mode, the primary replica commits transactions without the acknowledgement that an asynchronous-commit secondary replica has written transaction log records to disk.
Synchronous-Commit Mode
Similarly, availability replica using synchronous-commit mode is called synchronous-commit replica. In this mode, the primary replica commit transactions after waiting for the acknowledgement that synchronous-commit replica has written transaction log records to disk.
Types of Failover are as Follows
The role of primary and secondary replica can be interchanged in a method called failover. During a failover, the target secondary replica transitions to the primary role making the new primary replica. After that, the new replica database makes its database online like primary database so that client applications can connect to it. The former primary replica transitions to secondary role when it is available making it secondary database. The process of data synchronization continues.
- Planned Manual Failover (No data loss): It occurs after a failover command is issued by database administrator and cause a transition from synchronized secondary replica to primary role & from primary replica to secondary role.
- Automatic Failover (No data loss): It happens in response to a failure causing transition of synchronized secondary replica to primary role and from primary replica to secondary role.
- Forced Failover (with possible data loss): It is the type of failover that may lead to loss of data. It can be initiated manually and can act as disaster recovery option.
Limitations on Using The WSFC With Alwayson Availability Groups
Windows Server Failover Cluster Manager should not be used for manipulating Alwayson Availability Groups such as:
- Not to add or delete resources for the Availability Groups
- Never change any Availability Group properties, which are changed automatically by the Availability Group.
- Windows Server Failover Cluster Manager should not be used for moving Availability Groups to various nodes or to failover Availability Groups.
Latest Features of SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
It’s crucial for users to understand the Always On feature in SQL along with differences in AG & FCI. Now that we covered that, it’s unfair to not discuss its features of it. Now, from the 2016 SQL Server, it introduced two new features in Availability Groups.
- AlwaysOn Basic Availability Groups (AlwaysOn BAG)
- AlwaysOn Distributed Availability Group (AlwaysOn DAG)
Always On Basic Availability Groups – BAG
The Always On feature came in the 2016 edition, with the name BAG. At first, it looks similar to the usual AG. However, the BAG has the potential of using only the subsets of features when we compared it to the original AG in the SQL enterprise edition. For an instance, we can specify that the BAG only allows having two replicas that are primary & secondary. Understanding what is Always On SQL Server becomes easy when we dive deeper into technologies like this.
When we come to the failover support part, the BAG only provides supports for a single database by replacing the deprecated database mirroring.
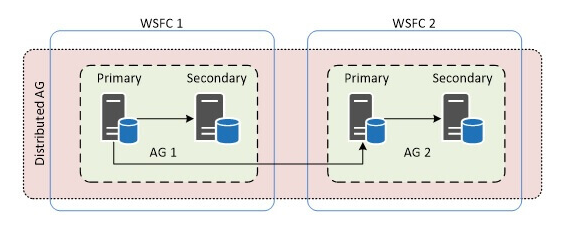
AlwaysOn Distributed Availability Groups – DAG
Now, when we look at the DAGs, these are loosely coupled groups of AGs. Over the two different AGs is where the AlwaysOn DAG runs. It directly indicates that it is under under two different WSFCs respectively. Therefore, their voting management, as well as quorum, are separate too.
Here, the secondary replicas of an AG exist in a different geographical region in comparison to the primary. Enabling the read only workload, for the remote regions is necessary. Simultaneously, get rid of potential network problems at the secondary site that might harm the primary site as well.
AlwaysOn Benefits in SQL Server You Can’t Miss
If users opt for the AlwaysOn feature in SQL Server, they can easily get the benefits that come along. Let’s have a look at these benefits in detail to know what is Always On SQL Server in detail.
- With the SQL Server enterprise edition, AlwaysOn AGs provide support for up to 9 available replicas. This simply means that each AG gets one primary & 8 secondary replicas seamlessly.
- Automatic Failover, Planned Manual Failover, and Forced Manual Failover are the names of various types of availability groups failover that users can choose for their more precise workflow.
- Users get the AlwaysOn dashboard where they can monitor all their AGs without any kind of hassles. Moreover, it also analyses the AlwaysOn policies along with availability replicas & databases.
- Along with the ability to encrypt & compress data files, it offers the high-performing transportation of data files with the utmost security standards.
- When it comes to page corruption, the AlwaysOn feature is very well capable to provide automatic page repair.
Environmental Set-Up Details of AlwaysOn SQL Server
For the Set-Up, users need to just follow the below-mentioned process in their respective order & they will find no hurdles in the entire process at all.
The very step for users is to set up two failover clusters as mentioned below:
Windows Failover Cluster – First
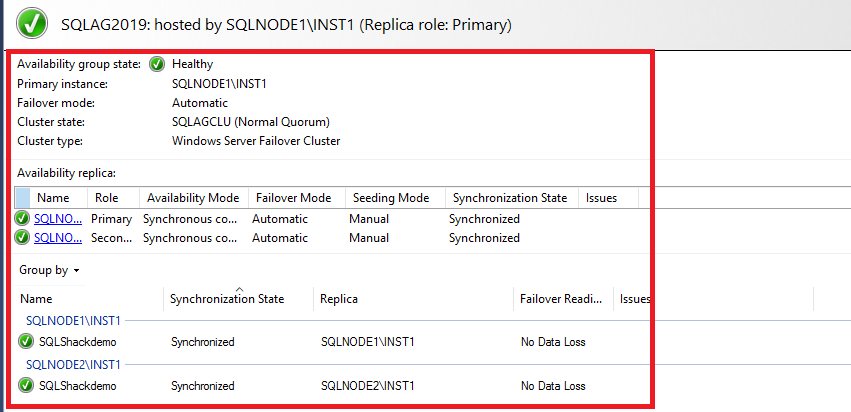
- In the first failover cluster, we can get two instances as [SQLNode1\INST1] and [SQLNode2\INST1].
- Here, users need to use the synchronous data synchronization between the primary & secondary SQL Server AlwaysOn AG of [SQLSHACKDEMO] database.
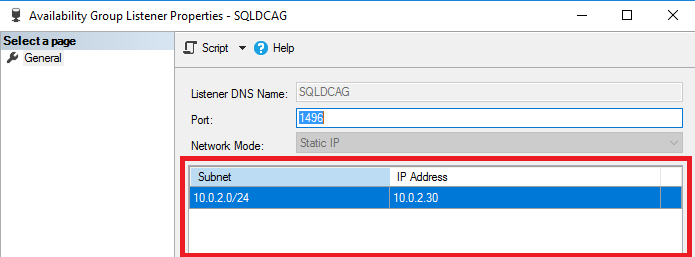
- Now, in order to connect with the primary replica, simply configure the SQL listener [SQLDCAG].
Windows Failover Cluster – Second
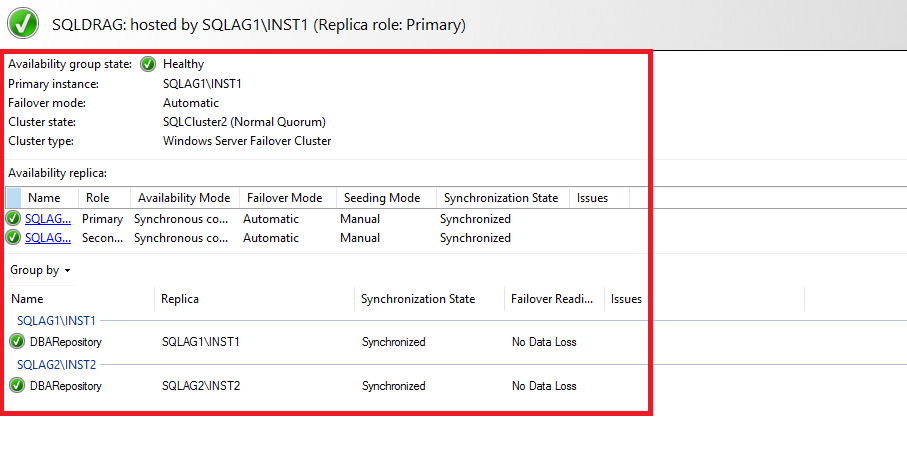
- Just like the failover cluster, in the second one also, users get two instances as [SQLAG1\INST1] and [SQLAG2\INST2].
- For the [DBARepository] database, simply use the synchronous data synchronization between primary & secondary replicas respectively.
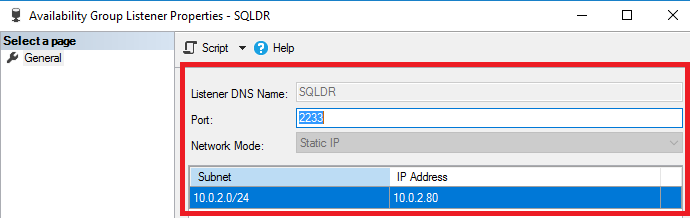
- Now, at last, configure the SQL listener [SQLDR] for establishing the connection with the primary replica.
We can say that both clusters are a significant part of [MyDemoSQL.COM] domain here. Therefore, users need to allow firewalls for both of them for enabling connections to another replica.
Evidently, users can see that their dashboard of Availability Groups is healthy in both groups.
SQLAG2019 Availability Group
SQLDRAG Availability Group
Conclusion
Finally, we hope that users are well aware of the AlwaysOn availability groups in SQL server in depth. Reading the entire guide can provide significant details to users as required.
